int lo_hi[0:15];
int c_style[16];
//Array structure: [int] [int] [int] [int] ... [int]
✅ Key Point: Can be declared low-to-high or using C-style syntax.
Calculating address width
parameter int MEM_SIZE = 256;
parameter int ADDR_WIDTH = $clog2(MEM_SIZE); //$clog2(256)=8
bit [15:0] mem[MEM_SIZE];
bit [ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] addr;
/*
mem
Index: mem[0] mem[1] mem[2] ... mem[255]
Data: [15:0] [15:0] [15:0] [15:0]
Bits: b15 ... b0 b15 ... b0 b15 ... b0 ... b15 ... b0
*/
✅ Key Point: $clog2(MEM_SIZE) gives number of bits needed to address MEM_SIZE elements.
Multi-dimensional arrays
int array2 [0:7][0:3]; //Verbose declaration
int array3 [8][4]; //Compact declaration
| Row \ Col | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | array2[0][0] | array2[0][1] | array2[0][2] | array2[0][3] |
| 1 | array2[1][0] | array2[1][1] | array2[1][2] | array2[1][3] |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 7 | array2[7][0] | array2[7][1] | array2[7][2] | array2[7][3] |
| ✅ Key Point: First index = row, second index = column. |
Unpacked Array
The example shown above are unpacked array. The values are stores in the
lower portion of the word, whereas the upper bits are unused.

Packed Array
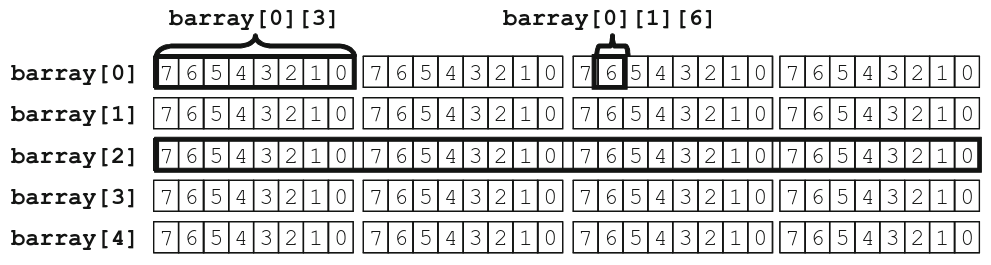
bit [3:0] [7:0] barray [5]; //5 elements: packed 4-bytes
bit [31:0] lw = 32'h0123_4567;
bit [7:0] [3:0] nibbles;
barray[0] = lw;
barray[0][3] = 8'h01;
barray[0][1][6] = 1'b1;
nibbles = barray[2];
✅ Key Point:
- Packed arrays store bits contiguously (like a vector).
- Allows bit- and byte-level slicing and indexing.